Topiramate side effects are a crucial aspect to consider when taking this medication. While topiramate is commonly prescribed for conditions like epilepsy and migraine headaches, it can also lead to a range of side effects, some of which can be serious. Understanding the potential risks associated with topiramate is essential for making informed decisions about your treatment plan.
This comprehensive guide delves into the common and serious side effects of topiramate, providing insights into their causes, management strategies, and the importance of open communication with your healthcare provider. By understanding the potential risks and taking proactive steps, you can work with your doctor to minimize the likelihood of experiencing adverse effects and maximize the benefits of this medication.
Introduction to Topiramate
Topiramate is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat epilepsy, but it also finds applications in managing migraine headaches and weight loss. It belongs to a class of medications known as antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) and works by modulating the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, specifically GABA and glutamate. This modulation helps to regulate nerve activity and reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
Understanding the potential side effects of topiramate is crucial before starting treatment. While the medication can be effective in managing various conditions, it’s essential to be aware of the possible risks and weigh them against the potential benefits. This information will empower you to make informed decisions about your treatment and work collaboratively with your healthcare provider to manage any side effects that may arise.
Common Side Effects of Topiramate: Topiramate Side Effects
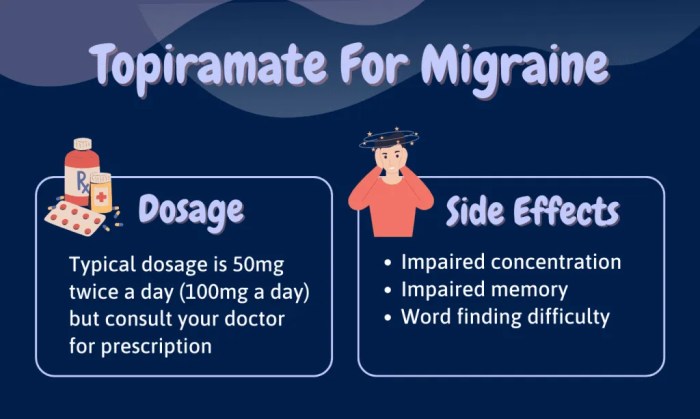
Topiramate, like many medications, can cause side effects. While these side effects are not experienced by everyone, it’s important to be aware of the possibilities and discuss any concerns with your doctor.
Common Side Effects of Topiramate
Topiramate can affect various body systems, leading to a range of side effects. These side effects are often mild and may subside over time.
| Side Effect | Frequency | Severity | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dizziness | Common | Mild to Moderate | Avoid activities that require alertness, such as driving or operating machinery. Stay hydrated. |
| Fatigue | Common | Mild to Moderate | Get enough sleep, eat a balanced diet, and exercise regularly. |
| Cognitive Impairment (e.g., memory problems, difficulty concentrating) | Common | Mild to Moderate | Talk to your doctor about strategies to manage cognitive side effects, such as using memory aids or adjusting the dosage. |
| Nausea and Vomiting | Common | Mild to Moderate | Take topiramate with food or a snack to reduce stomach upset. |
| Weight Loss | Common | Mild to Moderate | Talk to your doctor about ways to maintain a healthy weight. |
| Numbness or Tingling in the Hands and Feet | Common | Mild to Moderate | Avoid extreme temperatures. |
| Mood Changes (e.g., depression, anxiety) | Less Common | Mild to Severe | Talk to your doctor if you experience any mood changes. |
| Kidney Stones | Less Common | Moderate to Severe | Drink plenty of fluids to prevent kidney stones. |
| Increased Risk of Birth Defects | Rare | Severe | Topiramate is not recommended for women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. |
Serious Side Effects of Topiramate
While topiramate is generally safe and effective for many people, it’s important to be aware of the potential serious side effects. Some of these side effects can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention.
Serious Side Effects Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
It’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following serious side effects while taking topiramate:
- Severe allergic reactions: Symptoms include rash, hives, itching, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, difficulty breathing, or tightness in the chest.
- Metabolic acidosis: This condition occurs when the body produces too much acid. Symptoms include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, confusion, and coma.
- Kidney stones: These are hard deposits that can form in the kidneys. Symptoms include pain in the side or back, blood in the urine, nausea, vomiting, and fever.
- Glaucoma: This condition occurs when pressure builds up inside the eye. Symptoms include blurred vision, halos around lights, eye pain, and headache.
- Acute angle-closure glaucoma: This is a serious type of glaucoma that can lead to blindness if not treated promptly. Symptoms include sudden severe eye pain, blurred vision, nausea, and vomiting.
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN): These are rare but serious skin reactions that can be fatal. Symptoms include fever, sore throat, cough, and a painful rash that spreads and blisters.
- Suicidal thoughts or actions: Topiramate may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or actions in some people. If you have any thoughts of harming yourself, seek immediate medical attention.
Risks Associated with Topiramate
Topiramate is associated with several risks, including:
- Birth defects: Topiramate is a known teratogen, meaning it can cause birth defects in unborn babies. Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should avoid taking topiramate.
- Suicidal thoughts or actions: As mentioned earlier, topiramate may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or actions. It’s important to be aware of this risk and seek help if you experience any suicidal thoughts or feelings.
- Cognitive impairment: Topiramate can cause cognitive impairment, such as memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and slowed thinking. This can affect your ability to perform daily tasks.
- Drowsiness and dizziness: Topiramate can cause drowsiness and dizziness, which can increase the risk of falls and accidents.
Importance of Regular Monitoring and Communication with Healthcare Providers
It’s essential to monitor your health closely while taking topiramate and communicate any concerns or changes in your health to your healthcare provider. Regular checkups and blood tests can help monitor for potential side effects and ensure the medication is working safely and effectively.
Factors Influencing Side Effects
Several factors can influence the likelihood or severity of side effects from topiramate. These factors can be individual-specific, related to the medication itself, or a combination of both. Understanding these factors can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about topiramate use.
Age
Age can play a role in the risk and severity of topiramate side effects. For example, older adults may be more susceptible to certain side effects, such as cognitive impairment and dizziness. It’s important for healthcare providers to carefully monitor older adults taking topiramate for any signs of these side effects.
Gender
While the overall side effect profile of topiramate is similar for men and women, some studies suggest that women may be more likely to experience certain side effects, such as hair loss and mood changes.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Patients with certain underlying medical conditions may be at increased risk for specific side effects from topiramate. For instance, people with kidney or liver disease may experience more severe side effects due to the medication’s metabolism and elimination. Similarly, patients with a history of depression or anxiety may be more susceptible to mood changes or worsening of these conditions while taking topiramate.
Dosage, Topiramate side effects
The dosage of topiramate is another important factor influencing side effects. Higher doses are generally associated with a greater risk and severity of side effects. It’s essential to start with a low dose and gradually increase it as needed, under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Drug Interactions
Topiramate can interact with other medications, potentially increasing the risk of side effects. Some common examples include:
- Other anticonvulsants: Topiramate can increase the levels of other anticonvulsants in the blood, potentially leading to increased side effects.
- Oral contraceptives: Topiramate can decrease the effectiveness of oral contraceptives, increasing the risk of unintended pregnancy.
- Lithium: Topiramate can increase the levels of lithium in the blood, increasing the risk of lithium toxicity.
Managing Side Effects
Experiencing side effects from topiramate is common, but you can often manage them effectively. By understanding the potential side effects, you can work with your healthcare provider to find strategies that work best for you.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making simple changes to your lifestyle can sometimes help reduce side effects.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help prevent dehydration, which can worsen some side effects like fatigue and dizziness.
- Eat a balanced diet: A healthy diet can help maintain energy levels and reduce fatigue.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to improve energy levels and mood.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity can help manage fatigue and improve overall well-being. However, if you experience dizziness, it’s important to start slowly and avoid strenuous activities.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter medications can provide temporary relief for some side effects. However, it’s important to talk to your doctor before taking any new medications, as they may interact with topiramate.
- Antacids: For indigestion or heartburn, antacids like Tums or Pepto-Bismol can provide relief.
- Pain relievers: For headaches or muscle aches, over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be helpful.
- Antihistamines: For itching or skin rashes, antihistamines like loratadine or cetirizine can reduce symptoms.
Adjusting the Topiramate Dosage
In some cases, your healthcare provider may adjust your topiramate dosage to minimize side effects. This may involve lowering the dose or changing the frequency of administration. It’s crucial to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider
While many side effects are manageable, it’s important to contact your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following:
- Severe or persistent side effects that don’t improve with lifestyle modifications or over-the-counter medications.
- New or worsening side effects that concern you.
- Side effects that interfere with your daily activities.
Navigating the potential side effects of topiramate requires a collaborative approach between you and your healthcare provider. By staying informed, communicating openly, and actively managing your health, you can work together to ensure that the benefits of topiramate outweigh any potential risks. Remember, knowledge is power, and understanding the potential side effects of this medication is crucial for making informed decisions about your treatment plan and achieving optimal health outcomes.
Topiramate is a medication often prescribed for seizures and migraines, but it can have a range of side effects. Some people experience drowsiness, dizziness, or even weight loss. If you’re dealing with these side effects, it’s important to talk to your doctor. They can help you manage the side effects and determine if the medication is right for you. For example, if you’re experiencing financial difficulties due to the cost of your medication, you might need to consider legal options like a land lawyer near me.
Ultimately, your health and well-being are paramount, so it’s crucial to make informed decisions about your treatment plan.